PURPOSE: C4BP-based biologics as novel immunomodulators
Problema a Solucionar
The present anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive drugs, in an attempt to restore the immune homeostasis from patients suffering from immune-inflammatory processes such as GvHD, autoimmune diseases and transplant rejection, induce relevant and non-specific adverse events. Moreover, current biologic treatments for acute and chronic immune-inflammatory conditions and, particularly, autoimmune diseases, fall short of expected complete remission, due to its low efficacy and relevant and non-specific adverse events. The medical need for new treatments thus remains great–as does the potential market for a widely beneficial therapy. That is, novel immunomodulatory agents are needed, with increased potency, selectivity and safety profiles.
Estado de la tecnología
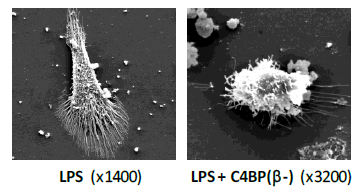
We have confirmed the immunomodulatory activity of C4BP (β-) over inflammatory DCs and macrophages. Moreover, we have successfully demonstrated the safety and the efficacy of low-dose, subcutaneous administration of C4BP (β-) to ameliorate autoimmune lupus nephritis in an experimental systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) mouse model (manuscript submitted).
In additional pre-clinical assays of inflammatory bowel disease and arthritis we have also shown the therapeutic potential of subcutaneous low-dose C4BP (β-) administration. In this last case, C4BP (β-) outperformed the anti-TNF Enbrel® (etanercept), a biologic standard-of-care for rheumatoid arthritis treatment.
Novel biologic C4BP (β-) analogues with improved production facility, and increased efficacy and safety profiles are ongoing.
Contexto
The breakdown of immune self-tolerance is the underlying cause of autoimmune pathology, which remains a major burden on health systems around the world. Thus, it is desirable to develop personalized treatments that allow for the specific blockade of the deleterious effects of self-reactive immune cell function and induce immune tolerance. We have recently identified a novel and powerful anti-inflammatory and tolerogenic activity in the minor C4BP isoform, C4BP (β-), that is not linked to its known function as soluble inhibitor of the complement system. C4BP (β-) is physiologically up-regulated under acute phase conditions. Thus, C4BP (β-)-based immunomodulation acts selectively over inflammatory phagocyte precursors promoting operational tolerance and, analogously to antibodies, is very stable in the circulation.
Tecnología
We have shown that the complement inhibitor isoform C4BP (β-) is able to induce an anti-inflammatory and tolerogenic state in monocyte-derived human dendritic cells (DCs) (Olivar et al. (2013) J Immunol. 190: 2857-72). This physiological immunomodulator overcomes the side effects of the present immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory drugs, and enables to perform pharmacological therapy (direct C4BP (β-) administration), or cell therapy using ex vivo C4BP (β-)-conditioned DCs.
Our current research involves:
1) Performing transcriptomic, proteomic, and functional analyses to assess the molecular mechanism of C4BP (β-) signaling in phagocytes.
2) Confirming the therapeutic potential of C4BP (β-) and analogues as biological immunomodulators in animal models of autoimmunity.
Autores
Aran J. M. (IDIBELL)
Technology Readiness Level
Technology fully validated in the lab.
Qué buscamos?
Licensing, co-development or investment for spin-off creation.
