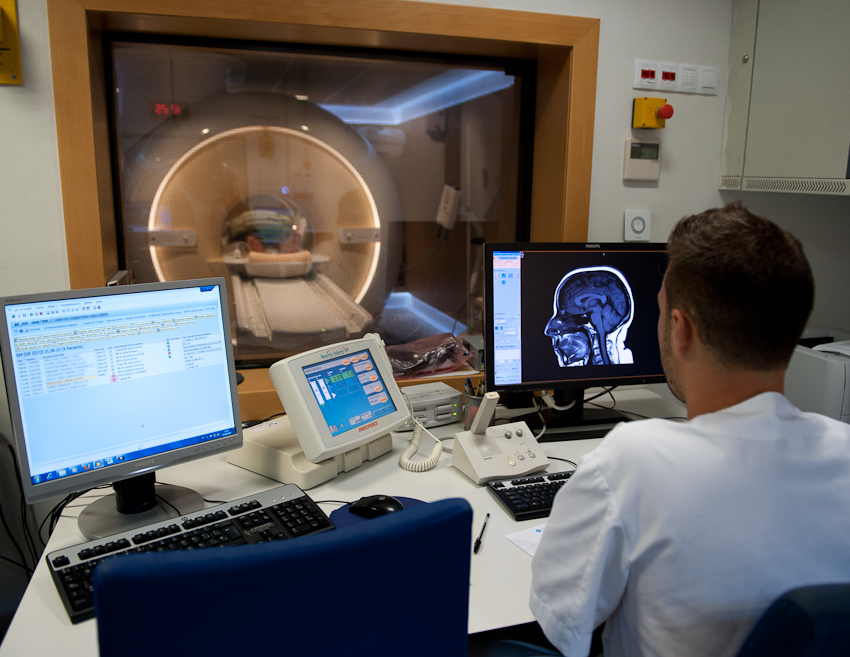
The Department of Psychiatry, University Hospital of Bellvitge (HUB) and the Institute of Diagnostic Imaging (IDI) have successfully performed the first cerebral MRI to a patient with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) treated with deep brain stimulation. This therapy involves the implantation of two electrodes in the brain, thats was the reason why individuals carrying them could not be subjected to standard neuroimaging scans safely.
Since April 2015 systems deep brain stimulation (DBS for its acronym in English) of the company Medtronic are CE marked (European Conformity) for compatibility standard (or whole body) MRIs. These systems incorporate radio frequency filter capacitors, a technology that dissipates the energy emitted by the resonance. It also allows the devices to continue activated in bipolar mode while the diagnostic test is performed.
Dr. Eva Real, the Department of Psychiatry University Hospital of Bellvitge, has coordinated the completion of the first whole body MRI in Spain to a patient with OCD treated with deep brain stimulation. “MRI is usually the best method to obtain images of any part of the body in order to diagnose diseases or control existing diseases, but so far its use was very limited for patients with DBS system,” he says. Considering that these patients have the same conditions as everyone else, the possibility of undergoing an MRI is vital to your health. Neuroimaging scans are also useful for monitoring the implementation of electrodes and to further research of OCD.
FIS research project of the Institute of Health Carlos III
The resonance practiced in the University Hospital of Bellvitge is part of a research project FIS led by Dr. Jose Manuel Menchón, head of the research group in psychiatry and mental health at IDIBELL, aimed at finding predictors of response to therapy, is ie to know which patients are more likely to respond to treatment before operating.
Reference in Spain
Bellvitge University Hospital is the Spanish center with more experience in the treatment of resistant OCD with DBS. This technique is also used in other neurological diseases (Parkinson, epilepsy, essential tremor and dystonia) and involves the implantation by neurosurgery, brain-pole two electrodes connected to a pulse generator that is placed in the chest or abdomen subcutaneously, and that controls electrical activity in the brain. Neuromodulation allows a normalization of the abnormal brain activity and an improvement of symptoms in 2 out of 3 of operated patients. The effectiveness of treatment depends largely on the skill of the neurosurgeon to precisely position the electrodes in areas of interest, and the team’s experience in psychiatry, which has to be specialized in the treatment of OCD and specifically trained in DBS. Since 2007 the Bellvitge University Hospital has treated 23 patients with this technique.
OCD affects between 2 and 3% of the world population. It is chronic fluctuating course of mental disorder characterized by the presence of intrusive thoughts (obsessions) that sometimes are accompanied by repetitive behaviors (compulsions). The most frequent pathological obsessive themes are checking, washing and cleanliness, order and the need for symmetry, aggressive thoughts and / or unwanted sex and the need to ask, confess or accumulate. The first line treatment is pharmacological and psychological, but approximately 10% of patients are resistant to all treatments and maintain disabling, chronic and deteriorating symptoms. It is in this group when it has to assess the possibility of surgery. OCD is a mental disorder with greater evidence of dysfunction in specific neuronal circuits and hence potentially treatable by DBS.